

Published on May 26, 2025, by Admin in the Luo Lab

Our lab recently published a research article titled “Comprehensive analysis across mammalian tissues and cells decipher the underlying mechanism of m6A specificity” in RNA. Congratulations to Guo-Shi Chai! This work systematically evaluates 193 published m6A-seq datasets to identify ~1.5 million high-confidence m6A sites in human and mouse, revealing distinct characteristics and functional roles of m6A across different cell lines and tissues.
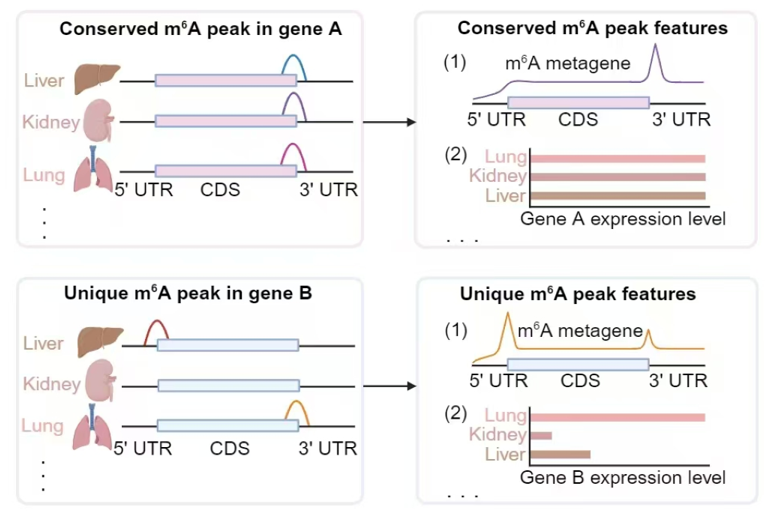
N6-methyladenine (m6A) stands out as the most prevalent internal chemical modification on mammalian mRNA, playing a vital role in diverse biological processes. However, the characteristics of m6A across different cell lines and tissues remain poorly understood. In this study, we systematically evaluated 193 published m6A-seq datasets using newly established quality metrics, identifying ~1.5 million high-confidence m6A sites in human and mouse. By categorizing m6A sites into different consistency levels, we observed that those with high consistency levels were enriched near mRNA stop codons and the 5’ end of lncRNA, interacted more frequently with known m6A-binding proteins, and influenced mRNA/lncRNA expression homeostasis. Furthermore, the promoters of genes marked by these consistent sites exhibited higher CpG density, with METTL3 preferentially binding to these regions. Conversely, low-consistency or unique m6A sites were enriched near mRNA start codons and distributed evenly across lncRNA, interacting with newly discovered m6A-binding proteins. These findings enhanced our understanding of the diverse characteristics and potential functional roles of m6A in mammals.